GetApp offers objective, independent research and verified user reviews. We may earn a referral fee when you visit a vendor through our links.
Our commitment
Independent research methodology
Our researchers use a mix of verified reviews, independent research, and objective methodologies to bring you selection and ranking information you can trust. While we may earn a referral fee when you visit a provider through our links or speak to an advisor, this has no influence on our research or methodology.
Verified user reviews
GetApp maintains a proprietary database of millions of in-depth, verified user reviews across thousands of products in hundreds of software categories. Our data scientists apply advanced modeling techniques to identify key insights about products based on those reviews. We may also share aggregated ratings and select excerpts from those reviews throughout our site.
Our human moderators verify that reviewers are real people and that reviews are authentic. They use leading tech to analyze text quality and to detect plagiarism and generative AI.
How GetApp ensures transparency
GetApp lists all providers across its website—not just those that pay us—so that users can make informed purchase decisions. GetApp is free for users. Software providers pay us for sponsored profiles to receive web traffic and sales opportunities. Sponsored profiles include a link-out icon that takes users to the provider’s website.
Authentication in Cybersecurity: A Primer for Small Businesses
Lay the foundation of cybersecurity for your small business with this 101 guide to authentication.

Unlocking your smartphone using your face ID, entering your username and password to log in to your work laptop, or inputting a one-time password (OTP) to access your business email—these digital rituals are all examples of user authentication.
Authentication is a critical component of enterprise cybersecurity, yet many small businesses don’t fully understand its importance. Our 2022 Biometrics Survey* reveals that 55% of businesses use multi-factor authentication to secure all of their business applications.
If you're a small-business owner looking to up your cybersecurity game, it's time to get serious about authentication. In this article, we explain what authentication is and why it's such a crucial aspect of small-business data security. So, let’s dive into the fundamentals of authentication—an essential chapter in cybersecurity.
What is authentication in cybersecurity?
Authentication refers to the process of verifying the identity of a user or device to secure access to sensitive information and systems. The authentication process involves presenting a set of credentials, such as a username and password, and verifying that they match the records stored in the company database.
By implementing strong authentication measures, you can safeguard your small business's confidential data and devices from unauthorized access and potential cybersecurity threats.
What are the different types of authentication?
Authentication is not limited to just passwords. In recent years, the authentication process has expanded further to verify more personal user information—for example, biometrics such as fingerprint and face scan—to protect business data, networks, and servers from hackers.
Let’s go through a few other metrics that can be used to authenticate users and devices:
Two-factor authentication requires a user to enter two sets of credentials, such as a password and an OTP sent to their phone, to authenticate their identity.
Biometrics authentication requires a user to provide their unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprint or iris pattern, as a form of identification.
Multi-factor authentication requires a user to enter more than two sets of verification proofs, such as a password, an OTP, and a fingerprint scan.
Single sign-on (SSO) authentication allows a user to access multiple systems or services by logging in once using a single set of credentials.
Certificate-based authentication uses a digital certificate, such as a secure sockets layer (SSL), to verify the identity of a user or device.
Token-based authentication uses a unique token, such as a USB or an OTP, to verify the identity of a user or device and secure access to sensitive information.
To learn more about these different types of authentication, check out this article.
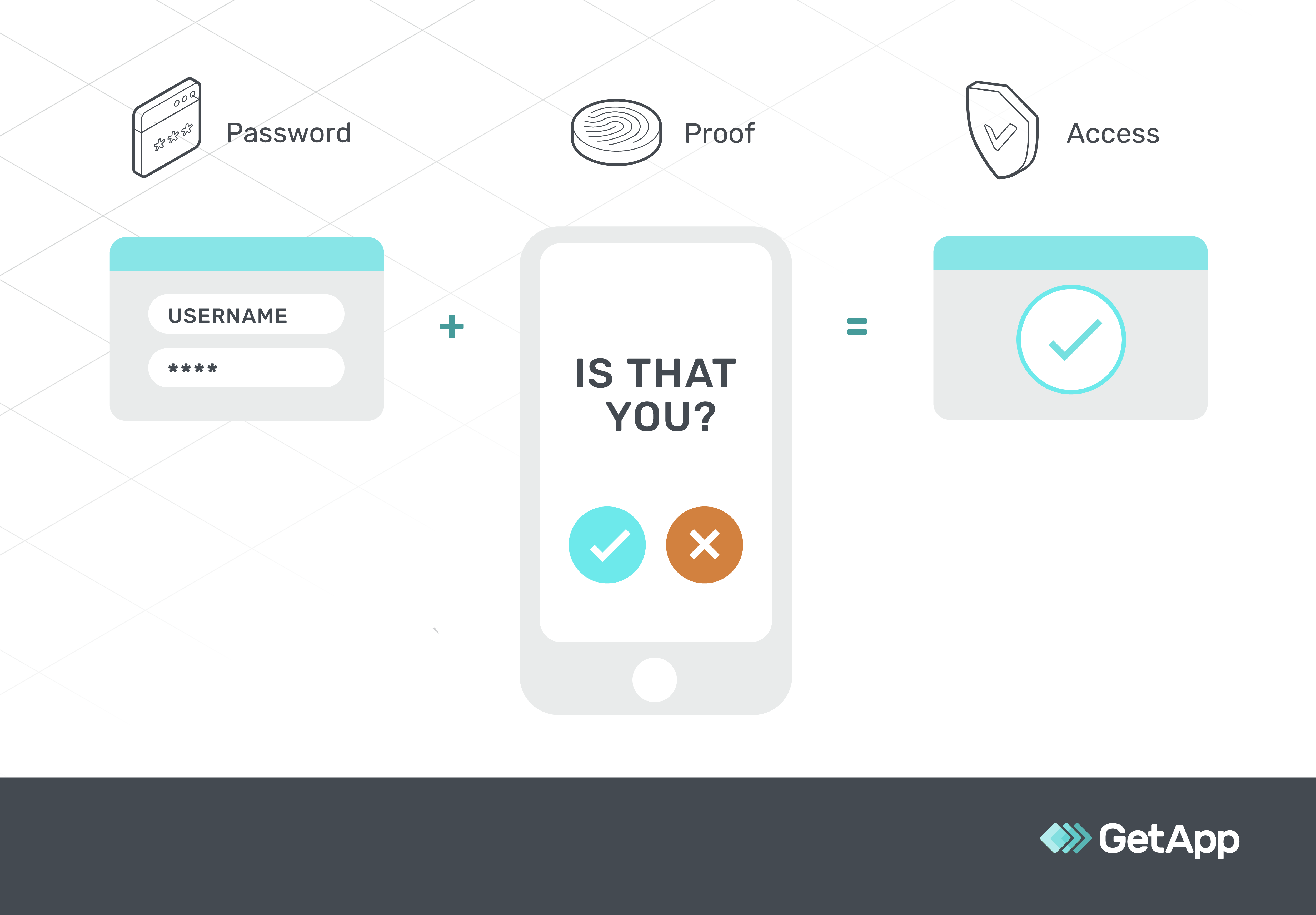
Diagrammatic representation of how mobile authentication works
What are the 3 main authentication factors?
An authentication factor refers to the evidence a user or device has to present to authenticate their identity. There are three main factors of user authentication: something they know (e.g., a password), something they have (e.g., a security token or smartcard), and something they are (e.g., biometrics).
Knowledge factor (something you know): It’s the most common type of authentication factor and verifies your identity by confirming any confidential information you remember, such as a username and password.
Possession factor (something you have): This authentication factor verifies your identity using a unique object you possess, such as a smartphone or token device. While this eliminates the risk of forgetting passwords, it also means you need to have the object with you at all times.
Inherence factor (something you are): This authentication factor verifies your identity through biometric characteristics, such as fingerprint, voice, and iris patterns. While it’s more secure than other types of authentication factors, it can also be expensive.
Note: Location (somewhere you are) and time (what time it is) are often considered additional authentication factors, but the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) [1] suggests they’re better categorized as security controls or supplemental authentication.
That’s because you can't verify someone's identity based solely on where they are or when they are accessing a system. For example, if two individuals are in the same location, it doesn't mean they are the same person. Therefore, location alone can't be used as a valid identifying factor, and the same applies to time.
They can only be applied as additional layers of secure access control to supplement the primary authentication factors. For example, you can schedule access during set hours of the day or week, or use location data such as GPS coordinates and IP address to spot anomalous activities.
What are the benefits of authentication for your small business?
Let's look at the benefits of authentication and its importance in protecting your IT systems from unauthorized access while safeguarding sensitive information.
Eliminates the risk of weak passwords
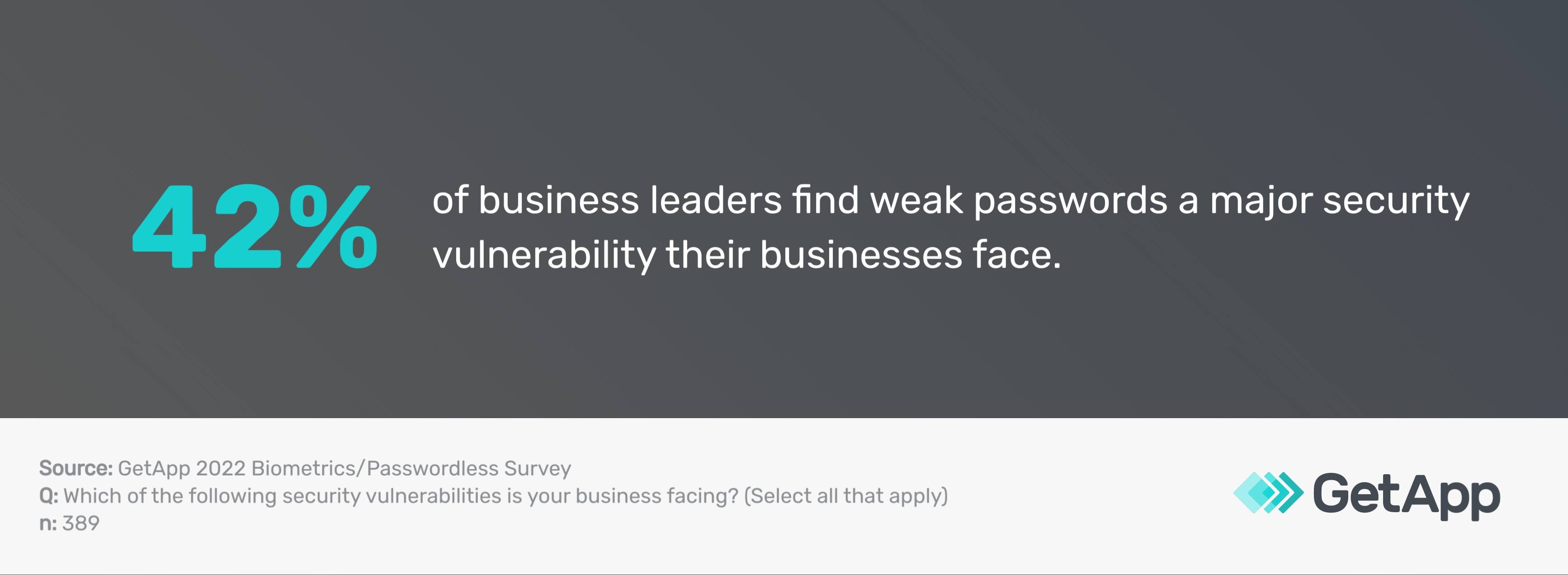
According to our 2022 Biometrics Survey*, 42% of business leaders consider weak passwords a significant security vulnerability for their organization. By implementing authentication practices, you can eliminate the potential risks posed by weak passwords and secure your business's sensitive information.
Tips to leverage this benefit:
Implement two-factor authentication to include an additional layer of security besides the usual password. Our 2022 Data Security Survey** confirms that 91.65% of businesses use two-factor authentication to make it harder for hackers to gain access to their systems and data.
Use passwordless authentication methods such as biometrics, phone-based authentication, and security keys to eliminate the need for passwords. Our 2022 Biometrics Survey* confirms that 82% of business leaders are ready to adopt passwordless authentication methods.
Regularly review and update user access controls to enhance security and minimize the risk of a security breach. Promote strong password policies through periodic reviews, employee education, and strict enforcement.
Protects your business from data breaches
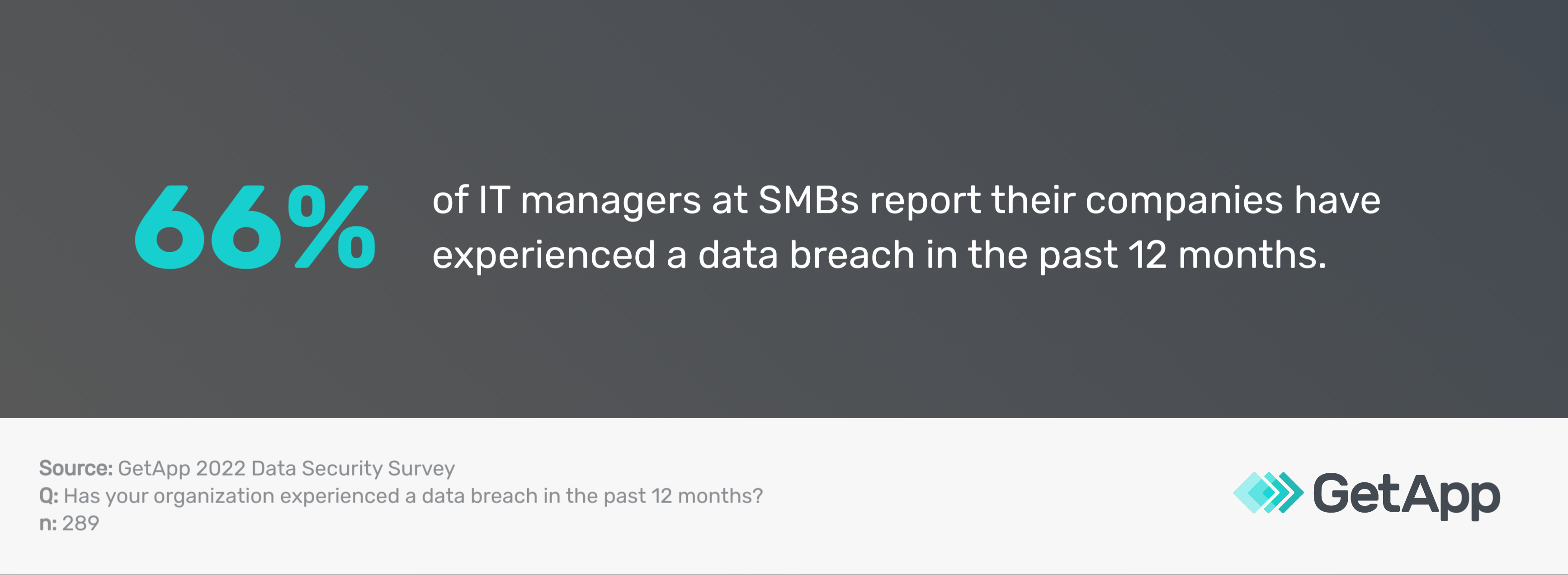
Our 2022 Data Security Survey** reports that 66% of businesses have fallen victim to a data breach in the past year. Proper authentication measures can safeguard your small business from cybersecurity threats such as data breaches by verifying user identity and granting access only to authorized individuals.
Tips to leverage this benefit:
Implement multi-factor authentication to protect your systems and data from unauthorized access. Our 2022 Biometrics Survey* confirms that 95% of business leaders say their company uses multi-factor authentication for at least some business applications; 55% say they use it for all applications.
Train your employees on how to properly use authentication systems to prevent hacking or unauthorized access attempts. Our 2021 Security Awareness Training Survey*** reveals that 53% of companies provide security awareness training to their employees more than once a year.
Conduct regular security assessments to identify and remediate vulnerabilities such as unpatched software or forced system login attempts in your authentication systems and networks.
Helps mitigate insider risks
Data breaches can come from various sources, including insiders such as your employees. The results of our 2022 Data Security Survey** emphasize the potential data safety threats posed by employees.
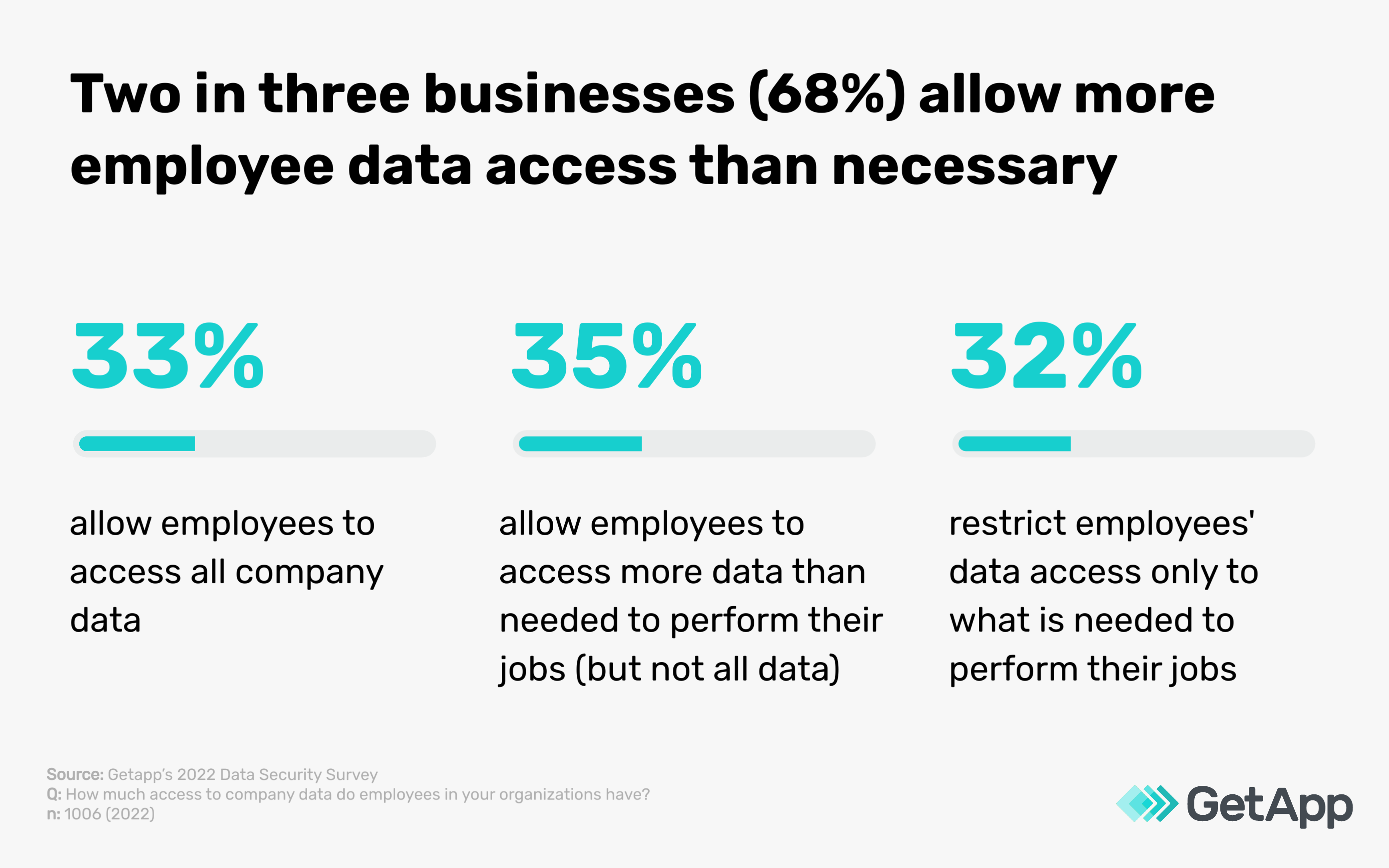
Thirty-three percent of businesses grant their employees full access to all company data, and 35% allow access to more data than what’s necessary for their employees’ job function. Only 32% limit employee data access to the minimum required for their job duties. These stats highlight the need for proper authentication measures to mitigate the risk of sensitive information being misused, leaked, or shared unintentionally by internal users.
Tips to leverage this benefit:
Implement role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication to limit data access to only necessary employees and roles. This will revoke access for users who don’t directly work with the data and reduce the chances of insider risk from unauthorized users.
Use multi-factor authentication to enhance the security of your in-house communication channels. MFA will secure the sensitive data shared between authenticated co-workers and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Implement a data loss prevention (DLP) solution with two-factor or multi-factor authentication to automatically identify and block sensitive data from leaving your organization through email, cloud storage, and other channels, thereby reducing the risk of insider data breaches.
Ready to ramp up cybersecurity with authentication?
Authentication is a game changer when it comes to cybersecurity for your small business. It's like having a security guard at the door, making sure the right people have access to your sensitive information, and keeping the intruders out.
However, despite the many benefits of authentication, it's important to weigh its potential drawbacks so you can make an informed decision. Let’s conclude with this quick sum-up:

Want to learn more about how to take your small-business cybersecurity to the next level? Check out these resources:
Methodologies
*GetApp conducted the 2022 Biometrics Survey in January 2022 among 974 consumers, including 389 business leaders who reported management responsibilities or above, to learn about attitudes toward biometrics and the use of multi-factor authentication by U.S. businesses.
**GetApp conducted the 2022 Data Security Survey in August 2022 to gauge the general state of cybersecurity at U.S. businesses and understand the use of various data protection controls among 1,006 respondents who reported full-time employment. 289 respondents identified as their company's IT security manager.
***GetApp conducted the 2021 Security Awareness Training Survey on November 2-4, 2021, among 573 respondents to learn more about security training practices at U.S. companies. All respondents indicated full employment and that they engage in security awareness training at least once per year.
Source
1. Digital identity guidelines, National Institute of Standards and Technology

Bhavya Aggarwal

