GetApp offers objective, independent research and verified user reviews. We may earn a referral fee when you visit a vendor through our links.
Our commitment
Independent research methodology
Our researchers use a mix of verified reviews, independent research, and objective methodologies to bring you selection and ranking information you can trust. While we may earn a referral fee when you visit a provider through our links or speak to an advisor, this has no influence on our research or methodology.
Verified user reviews
GetApp maintains a proprietary database of millions of in-depth, verified user reviews across thousands of products in hundreds of software categories. Our data scientists apply advanced modeling techniques to identify key insights about products based on those reviews. We may also share aggregated ratings and select excerpts from those reviews throughout our site.
Our human moderators verify that reviewers are real people and that reviews are authentic. They use leading tech to analyze text quality and to detect plagiarism and generative AI.
How GetApp ensures transparency
GetApp lists all providers across its website—not just those that pay us—so that users can make informed purchase decisions. GetApp is free for users. Software providers pay us for sponsored profiles to receive web traffic and sales opportunities. Sponsored profiles include a link-out icon that takes users to the provider’s website.
Penetration Testing Vs. Vulnerability Scanning—What's Best For SMBs?
Discover the right approach to fix the hidden security vulnerabilities in your small business that cybercriminals might exploit.

Both vulnerability scanning and penetration testing can help extract invisible anomalies. But which one should you pick for your small business? As an IT manager, you need to consider several factors rather than just cost to get the best results on your investment.
We interviewed Colleen Morrissey [1], acting director of information security at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, to help break down your options. She recommends factoring in your compliance goals, risk appetite, data sensitivity, and financial budget.
“Vulnerabilities are not the problem. They can be found and treated quickly. What matters is how you execute this operation. Can you afford a third-party ethical hacker to peek inside your data? Can you bear some hours of downtime? That's what makes your choice.”
—Colleen Morrissey, Acting director of information security at RPI

Colleen Morrissey, Acting director of information security at RPI
What is vulnerability scanning?
Vulnerability scanning identifies and assesses weaknesses in a computer system or network using vulnerability scanner software, such as missing software updates, unsecured network connections, outdated antivirus, weak passwords, and unauthorized access points.
It’s like a checkup for your IT systems to ensure everything is secure and running smoothly. By identifying and fixing issues, vulnerability tests help protect your IT resources from potential cyberattacks and keep your business data safe.
Two vulnerability scanning techniques
Vulnerability scans can be divided into two main categories: credentialed scans and non-credentialed scans.
| Credentialed scan | Non-credentialed scan | |
|---|---|---|
| Also known as | Authenticated scan | Unauthenticated scan |
| How it functions | Uses your login credentials to scan the internal components of IT systems, such as the database and internal file system. | Scans the external components of your IT systems, such as public IP addresses and email servers, without requesting your login credentials. |
| Cybersecurity vulnerabilities it can detect | Misconfigured system settings, internal application errors, and malware (viruses/trojans). | Loose network connections, unpatched (outdated) software, unsecure web services, hijacked DNS servers. |
| Scope of scan | Scans a wide range of in-system (internal) vulnerabilities. | Scans external vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers without valid login credentials. |
| Time and effort required | High | Low |
What is penetration testing?
Penetration testing is a cybersecurity practice where your IT team employs ethical hackers to penetrate (breach inside) your business's security infrastructure, and specific areas you request, such as applications, cloud, or online networks, using manual and automated processes.
This enables them to uncover weak spots and vulnerabilities that unethical hackers could exploit to disrupt your business operations. Once these vulnerabilities are found, penetration testers also assist your IT team in patching these security holes using various security and compliance software. Penetration testing doesn’t just help detect vulnerabilities but also understands the impact of cybercriminals exploiting them.
Three techniques of penetration testing:
Manual penetration testing: Security experts mimic real hacking scenarios to identify vulnerabilities in your systems using their expertise and creativity.
Automated penetration testing: Specialized security software systematically scans your IT infrastructure and networks to identify common security weaknesses. Unlike a vulnerability scanner, which merely detects known vulnerabilities, automated penetration testing tools go a step further by attempting to exploit these vulnerabilities, simulating the actions of an actual attacker to gauge potential impact.
Combination of manual and automated penetration testing: This blends human ingenuity and manual tests with the broad coverage of automated scans for comprehensive security checks.
Did you know?
Google, to date, has paid more than $45 million worth of bug bounty (reward price) to security professionals for finding critical vulnerabilities in its software and applications. [2] But never confuse a bug bounty program with penetration testing.
Bug bounty programs reward independent security researchers who find and report vulnerabilities. Penetration testing involves hiring professional cybersecurity testing teams (ethical hackers) to actively inspect your company’s IT and digital infrastructure for vulnerabilities.
Understand the difference between vulnerability scanning and penetration testing
Morrissey says there’s a thin line between these vulnerability identification approaches. Let’s compare them based on different factors.
1. Vulnerability scanning can be done with software while penetration testing requires more resources
Vulnerability scanners, whether used as standalone software or as a feature of cybersecurity software, work automatically to scan systems and applications to identify potential weaknesses. It analyzes configurations, system settings, and software versions, looking for known vulnerabilities based on large databases of historical flaws. Scanning is broad but not very deep. The tools identify possible vulnerabilities but don't confirm if they are actually exploitable.
How do cybersecurity software users feel about the kind of vulnerability scanning capabilities described above? We analyzed verified user ratings on GetApp to find out how important they find them.*

Penetration testing takes vulnerability identification to the next level by attempting to actively exploit weaknesses to prove if they are real vulnerabilities that pose a risk. Penetration testing leverages both automated scanning tools to conduct an initial broad search and manual techniques by human security experts, aka pen-testers. They use their skills and experience to probe for flaws thoroughly, confirm which ones are exploitable, and demonstrate potential impacts through simulated attacks.
This combined automated and manual approach allows penetration testing to cover a wider search area while going deeper through manual verification and exploitation. Morrissey highlights that penetration testing often finds vulnerabilities missed by automated scanning tools, such as insider threats and poor IT asset management.
In your small business, employ both automated scanning for breadth and manual testing for depth to implement a robust vulnerability identification program as part of a well-rounded cyber defense strategy.
2. Vulnerability scanning is generally more affordable
Because they rely on technology rather than human experts, vulnerability scanning services are usually less expensive. The trade-off is that they provide a broader but more shallow view of vulnerabilities. Penetration testing typically costs more due to the need for skilled security professionals to verify and exploit identified vulnerabilities manually.
A penetration test is approximately 2.5 times costlier than a vulnerability scan (Source)
So, while penetration testing has a higher price tag, organizations are paying for the knowledge and skills of these security professionals. Morrissey insists you evaluate the value of the services, not just the dollar amount, when comparing costs.
Penetration testers don’t just hone the ability to find vulnerabilities that automated scans may miss, but their detailed reports also provide remediation advice to help organizations strengthen security defenses. Consider the overall cost in tandem with the benefits provided when determining which security services best suit your small organization's needs and budget.
3. Penetration testing is comprehensive but can pose more risk
Vulnerability scanning only searches for potential flaws without exploiting them; thus, these automated scans pose very little to no disruption to your business systems and operations. Organizations can safely run scans frequently to identify possible weak points.
Penetration testing introduces more risk since the process involves security experts actively attempting to exploit vulnerabilities to prove if they are real. Depending on the type of testing, this exploitation can potentially cause service interruptions, system crashes, or data loss if proper precautions are not taken.
For a more detailed idea of how pentesting can be more disruptive for your small business, check out this case story below:
Matt Little [3], co-owner of Damien McEvoy Plumbing, wanted to uncover security loopholes in his small business while understanding how hackers operate, so he hired a security firm to run a penetration test on his small business. The process was eye-opening, providing insights into potential vulnerabilities and the world of ethical hacking.
However, an unexpected slip-up occurred during the testing. The security firm's aggressive probing of the system to simulate a real-world cyberattack inadvertently triggered a critical failure, crashing the system and disrupting warehouse stock records. Though most data was recovered, the incident left Matt questioning his decision to test.
For small-business owners considering pen-testing, this case story is a real-world example of the challenges and considerations involved. It's a reminder that while pen-testing can provide valuable insights, it's not without risks, and those risks must be carefully weighed.

Matt Little, Co-owner of Damien McEvoy Plumbing
Morrissey considers it critical for your small business to have contingency plans and precautions in place.

She mandates all these steps of proactive planning with your IT team. This allows you to get the benefits of penetration testing while minimizing the risks of disrupting your business and customers.
4. Penetration testing is comprehensive, but vulnerability scanning is still important
According to Morrissey, penetration testing is more comprehensive than vulnerability scanning. However, this does not mean it necessarily produces higher-quality results. Both approaches have a unique value.
As a small-business owner, you can run vulnerability scans yourself or through a partner to uncover common issues such as outdated software, misconfigurations, and missing patches. These are widespread vulnerabilities that scanners can easily detect.
In contrast, penetration testing by experts can find less obvious flaws such as insider data theft or sophisticated identity spoofing attacks. For example, your pentester may detect an employee stealing data by exploiting their access rights, or they may uncover a potential spoofing vulnerability by impersonating an executive during testing.
GetApp ran an Insider Threats Survey** in 2023 to understand the most common types of insider threats small businesses face and their frequency.
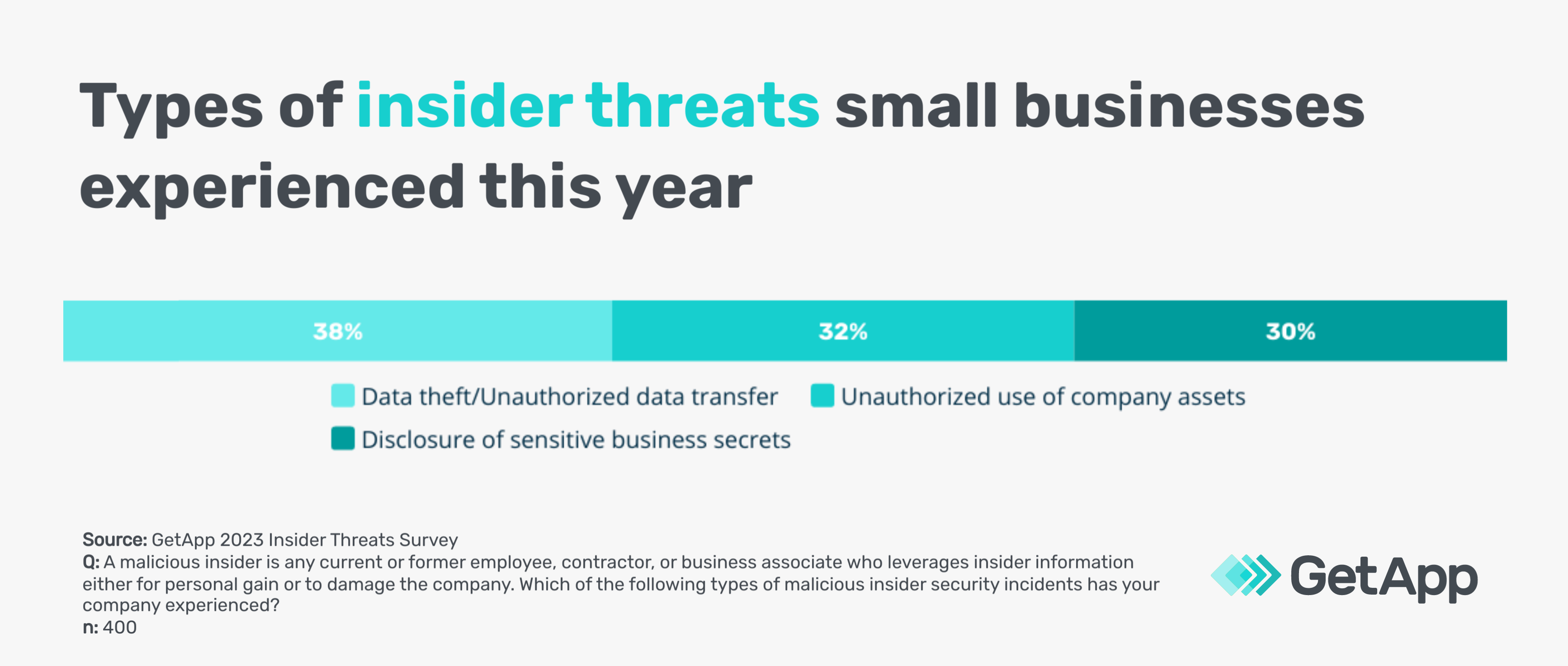
Morrissey cautions that all types of vulnerabilities pose risks. A flawed software patch process can be just as damaging as an insider attack. Prioritize remediating issues based on the potential business impact.
5. Penetration testing involves a manual style of report generation
Vulnerability scanning tools automatically generate reports after a scan. These reports contain high-level overviews of discovered vulnerabilities, compliance failures, and security misconfigurations across the environment. They may also provide remediation guidance for each finding (depending on your software subscription).
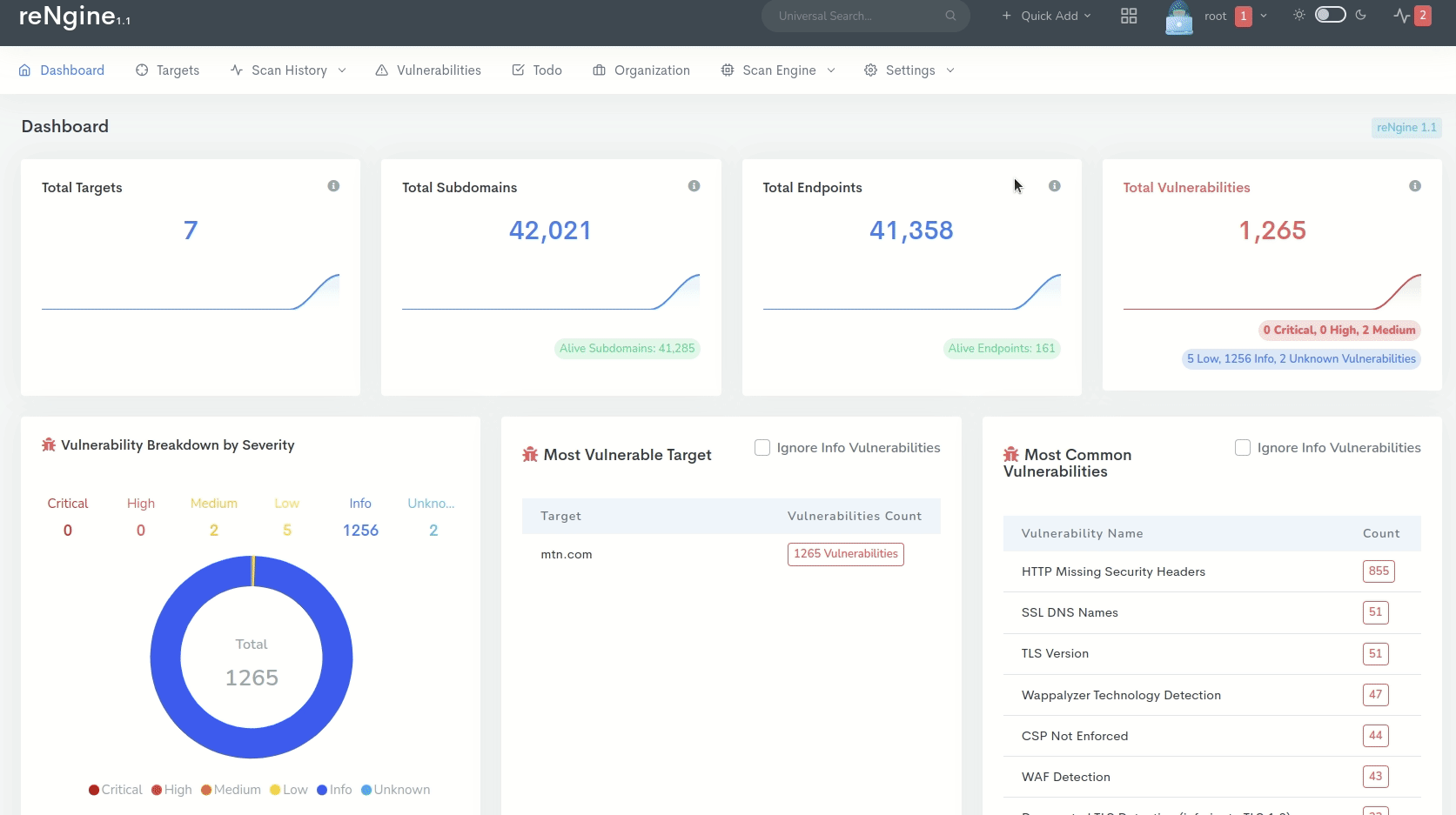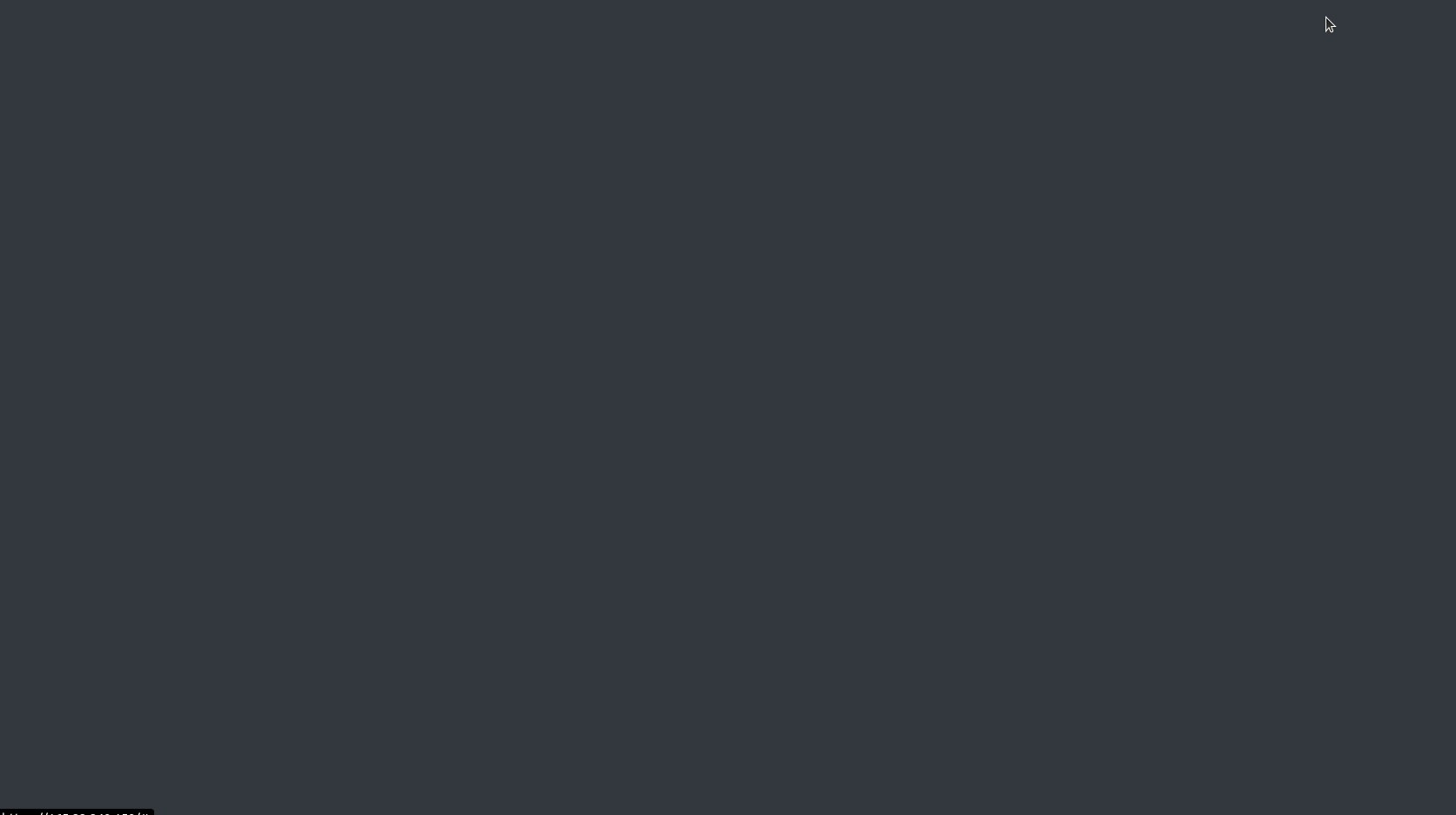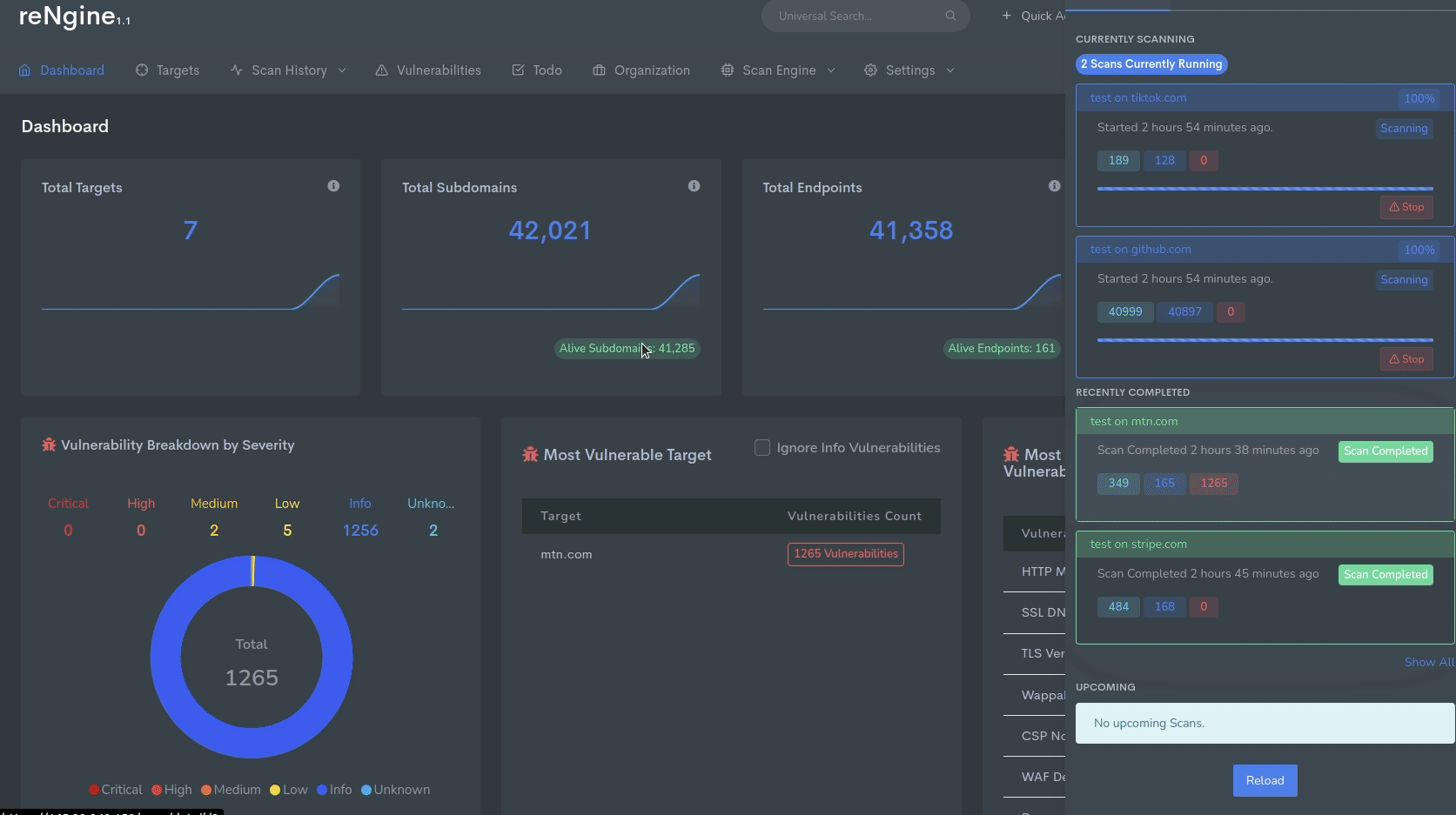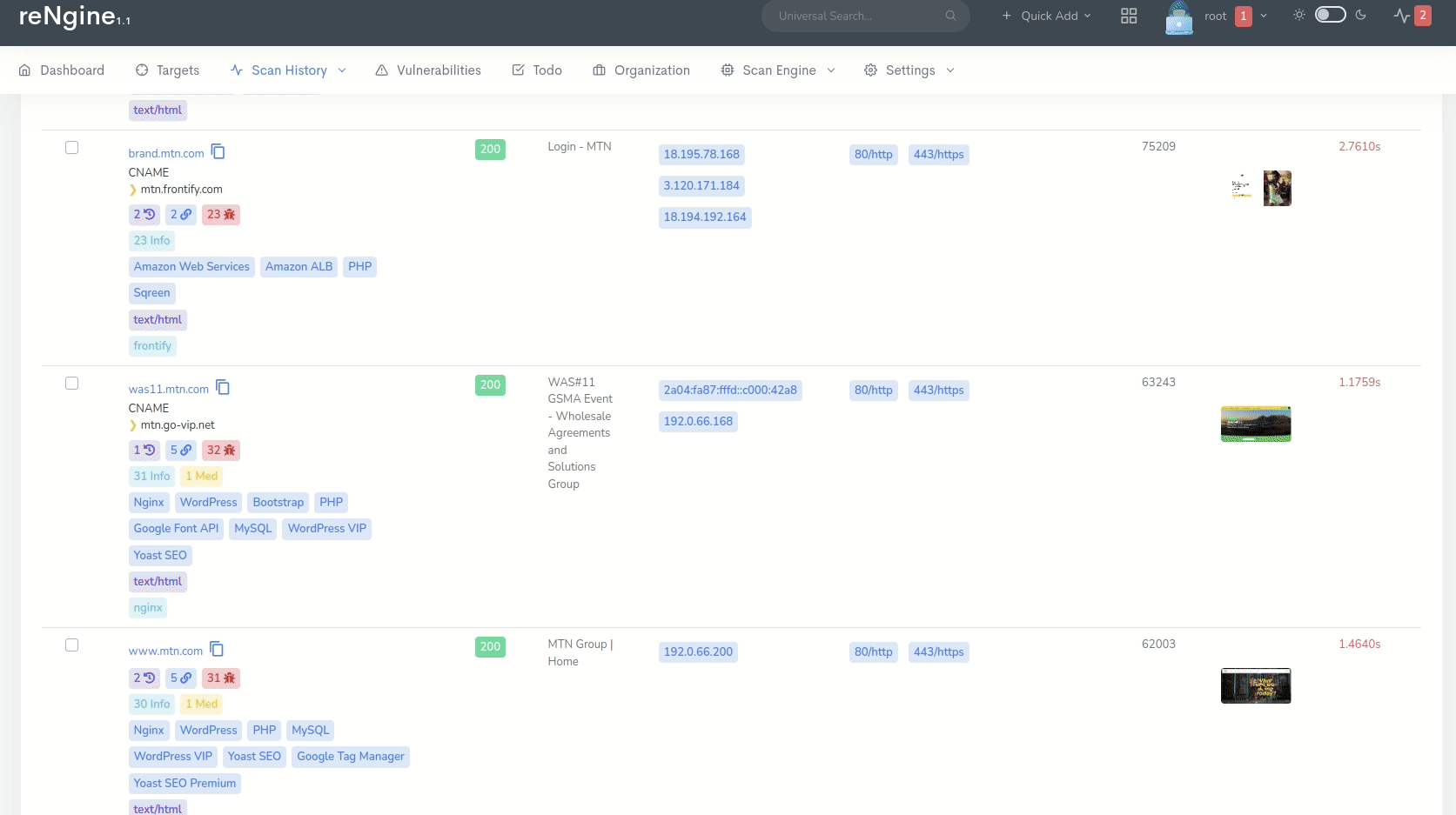
Vulnerability scanner displaying detected vulnerabilities [4]
Important note
Remember that vulnerability scanners, while incredibly useful, can sometimes generate false positives. For instance, they might flag in-app software updates as potential threats, which, in reality, pose no risk to your business. So, when reviewing and analyzing detected vulnerabilities, be discerning to ensure you don't waste your valuable resources and time.
In contrast, penetration test reports are manually created by security experts. They contain comprehensive details on each vulnerability successfully exploited, demonstrating how attackers could leverage them to harm the business. Testers will provide tailored remediation advice based on the unique context of the organization's environment and operations.
Morrissey explains it's crucial to review vulnerability and penetration test reports with your specific business in mind. A critical vulnerability for one company may be a lower risk for yours based on your systems and controls.
For example, an eCommerce site should prioritize fixing flaws that could expose customer data or disrupt sales. Similar issues may have less impact on a small marketing firm.
The point is—don't just fix everything by the book. Carefully evaluate findings affecting your small business operations, revenue, and reputation. This lets you focus on addressing the vulnerabilities that pose the most real significant risks.
By keeping your unique business context in mind as you review automated and expert testing reports, you can zero in on the most dangerous threats to your organization. This targeted remediation improves security while maximizing the use of available resources.
6. Differences in the remediation of vulnerabilities
Remediating vulnerabilities uncovered by scans and penetration tests requires capable in-house IT and security teams.
For vulnerability scan findings, internal staff such as network admins, database admins (DBAs), and developers can implement remediation based on their areas of expertise. For example, DBAs can patch database flaws while network engineers address vulnerable services.
For penetration test findings, the nuances of complex vulnerabilities may warrant outside help from the same testers who uncovered them. Morrissey says the ability of your penetration testing partner to assist with the remediation of sophisticated flaws, followed by their knowledge of subtle weaknesses, can prove invaluable for complete remediation. Just ensure you:
Ask your tester detailed questions about complex vulnerabilities. Don't assume your staff understands them.
Have your tester validate that their proposed remediation steps fully address the root cause.
Consider having your tester perform re-tests after remediation to verify the vulnerabilities are fixed.
Document the remediation process taken for future reference.
By leveraging internal IT expertise plus your penetration tester's knowledge, you can fully remediate vulnerabilities to harden your defenses.
You may want to check out: A 7-Step Penetration Testing Guide by a Security Director
Expert suggests a layered approach for your small business
Morrissey sees both penetration testing and vulnerability scanning as two sides of the same coin, each playing a crucial role in unmasking hidden vulnerabilities and bolstering your defenses against hackers.
If you're a small, homegrown business or a startup, Morrissey suggests starting with vulnerability scanning. It's more affordable and can be more of a do-it-yourself (DIY) process. You can consult a security expert to understand the identified vulnerabilities and discuss how best to address them.
But for mid-size to larger enterprises, with a larger workforce, sensitive data to safeguard, international clients to serve, and intellectual property to protect, penetration testing becomes more relevant.
We would advise you to start with GetApp’s security assessment template at the end of this article. It'll give you a snapshot of your business's security posture and help you identify potential vulnerabilities. From there, create a vulnerability management program that includes conducting vulnerability scans and addressing any issues found.
If you're still keen to leave no stone unturned after all that, consider a targeted penetration test. You could focus on areas you feel are most at risk, such as data storage systems, cloud-based asset repositories, or private company resources. This way, you can check if a hacker could still find a way in.
Remember that penetration testing can be conducted from inside and outside your business, resulting in a more comprehensive security assessment. But as Morrissey says, there's no 100% security in the world of cybersecurity. Keeping yourself and your team updated on best security practices is vital.
Sources
Colleen Morrisey, LinkedIn
Bug hunters, Google
Matt Little, LinkedIn
Methodology
* Users of cybersecurity software are asked to rate the importance of dozens of features that are offered in cybersecurity software products. For this analysis, we looked at 204 users who provided an importance rating for vulnerability scanning within the past two years (as of 20th August 2023).
** GetApp conducted this survey in March 2023 among 400 respondents to learn more about insider threats at U.S. businesses. All respondents were screened for leadership positions within their company.

Bhavya Aggarwal

